A study showed that scientists can wirelessly determine the path a mouse walks with a press of a button. Researchers at the Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, and University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, created a remote controlled, next-generation tissue implant that allows neuroscientists to inject drugs and shine lights on neurons deep inside the brains of mice. The revolutionary device is described online in the journal Cell. Its development was partially funded by the National Institutes of Health.
“It unplugs a world of possibilities for scientists to learn how brain circuits work in a more natural setting.” said Michael R. Bruchas, Ph.D., associate professor of anesthesiology and neurobiology at Washington University School of Medicine and a senior author of the study.
Highlights
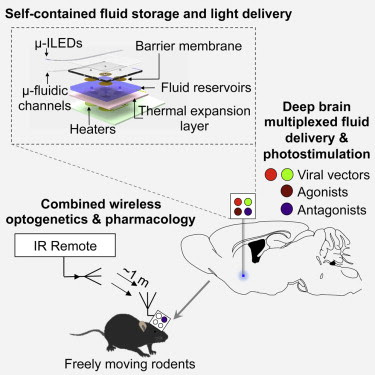
• Neural probes with ultrathin, soft microfluidic channels coupled to μ-ILEDs
• Optofluidic probes minimize tissue damage and are suitable for chronic implants
• Wireless in vivo fluid delivery of viruses, peptides, and small-molecule agents
• Combined wireless optogenetics with pharmacology for neural circuit dissection
Cell Journal – Wireless Optofluidic Systems for Programmable In Vivo Pharmacology and Optogenetics
The Bruchas lab studies circuits that control a variety of disorders including stress, depression, addiction, and pain. Typically, scientists who study these circuits have to choose between injecting drugs through bulky metal tubes and delivering lights through fiber optic cables. Both options require surgery that can damage parts of the brain and introduce experimental conditions that hinder animals’ natural movements.
To address these issues, Jae-Woong Jeong, Ph.D., a bioengineer formerly at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, worked with Jordan G. McCall, Ph.D., a graduate student in the Bruchas lab, to construct a remote controlled, optofluidic implant. The device is made out of soft materials that are a tenth the diameter of a human hair and can simultaneously deliver drugs and lights.
“We used powerful nano-manufacturing strategies to fabricate an implant that lets us penetrate deep inside the brain with minimal damage,” said John A. Rogers, Ph.D., professor of materials science and engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and a senior author. “Ultra-miniaturized devices like this have tremendous potential for science and medicine.”
With a thickness of 80 micrometers and a width of 500 micrometers, the optofluidic implant is thinner than the metal tubes, or cannulas, scientists typically use to inject drugs. When the scientists compared the implant with a typical cannula they found that the implant damaged and displaced much less brain tissue.
The scientists tested the device’s drug delivery potential by surgically placing it into the brains of mice. In some experiments, they showed that they could precisely map circuits by using the implant to inject viruses that label cells with genetic dyes. In other experiments, they made mice walk in circles by injecting a drug that mimics morphine into the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a region that controls motivation and addiction.
The researchers also tested the device’s combined light and drug delivery potential when they made mice that have light-sensitive VTA neurons stay on one side of a cage by commanding the implant to shine laser pulses on the cells. The mice lost the preference when the scientists directed the device to simultaneously inject a drug that blocks neuronal communication. In all of the experiments, the mice were about three feet away from the command antenna.
“This is the kind of revolutionary tool development that neuroscientists need to map out brain circuit activity,” said James Gnadt, Ph.D., program director at the NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS). “It’s in line with the goals of the NIH’s BRAIN Initiative.”
The researchers fabricated the implant using semi-conductor computer chip manufacturing techniques. It has room for up to four drugs and has four microscale inorganic light-emitting diodes. They installed an expandable material at the bottom of the drug reservoirs to control delivery. When the temperature on an electric heater beneath the reservoir rose then the bottom rapidly expanded and pushed the drug out into the brain.
“We tried at least 30 different prototypes before one finally worked,” said Dr. McCall.
Summary
In vivo pharmacology and optogenetics hold tremendous promise for dissection of neural circuits, cellular signaling, and manipulating neurophysiological systems in awake, behaving animals. Existing neural interface technologies, such as metal cannulas connected to external drug supplies for pharmacological infusions and tethered fiber optics for optogenetics, are not ideal for minimally invasive, untethered studies on freely behaving animals. Here, we introduce wireless optofluidic neural probes that combine ultrathin, soft microfluidic drug delivery with cellular-scale inorganic light-emitting diode (μ-ILED) arrays. These probes are orders of magnitude smaller than cannulas and allow wireless, programmed spatiotemporal control of fluid delivery and photostimulation. We demonstrate these devices in freely moving animals to modify gene expression, deliver peptide ligands, and provide concurrent photostimulation with antagonist drug delivery to manipulate mesoaccumbens reward-related behavior. The minimally invasive operation of these probes forecasts utility in other organ systems and species, with potential for broad application in biomedical science, engineering, and medicine.

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.