Radiation doses below about 100 – 200 mSv suppress cancer.
That bold, conventional wisdom-challenging statement is supported by an incredibly important paper titled Cancer risk at low doses of ionizing radiation: artificial neural networks inference from atomic bomb survivors published in the Journal of Radiation Research. It first appeared in an online version in December 2013.
Cancer risk at low doses of ionizing radiation remains poorly defined because of ambiguity in the quantitative link to doses below 0.2 Sv in atomic bomb survivors in Hiroshima and Nagasaki arising from limitations in the statistical power and information available on overall radiation dose. To deal with these difficulties, a novel nonparametric statistics based on the ‘integrate-and-fire’ algorithm of artificial neural networks was developed and tested in cancer databases established by the Radiation Effects Research Foundation. The analysis revealed unique features at low doses that could not be accounted for by nominal exposure dose, including (i) the presence of a threshold that varied with organ, gender and age at exposure, and (ii) a small but significant bumping increase in cancer risk at low doses in Nagasaki that probably reflects internal exposure to 239Pu. The threshold was distinct from the canonical definition of zero effect in that it was manifested as negative excess relative risk, or suppression of background cancer rates. Such a unique tissue response at low doses of radiation exposure has been implicated in the context of the molecular basis of radiation–environment interplay in favor of recently emerging experimental evidence on DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice and its epigenetic memory by histone marking.
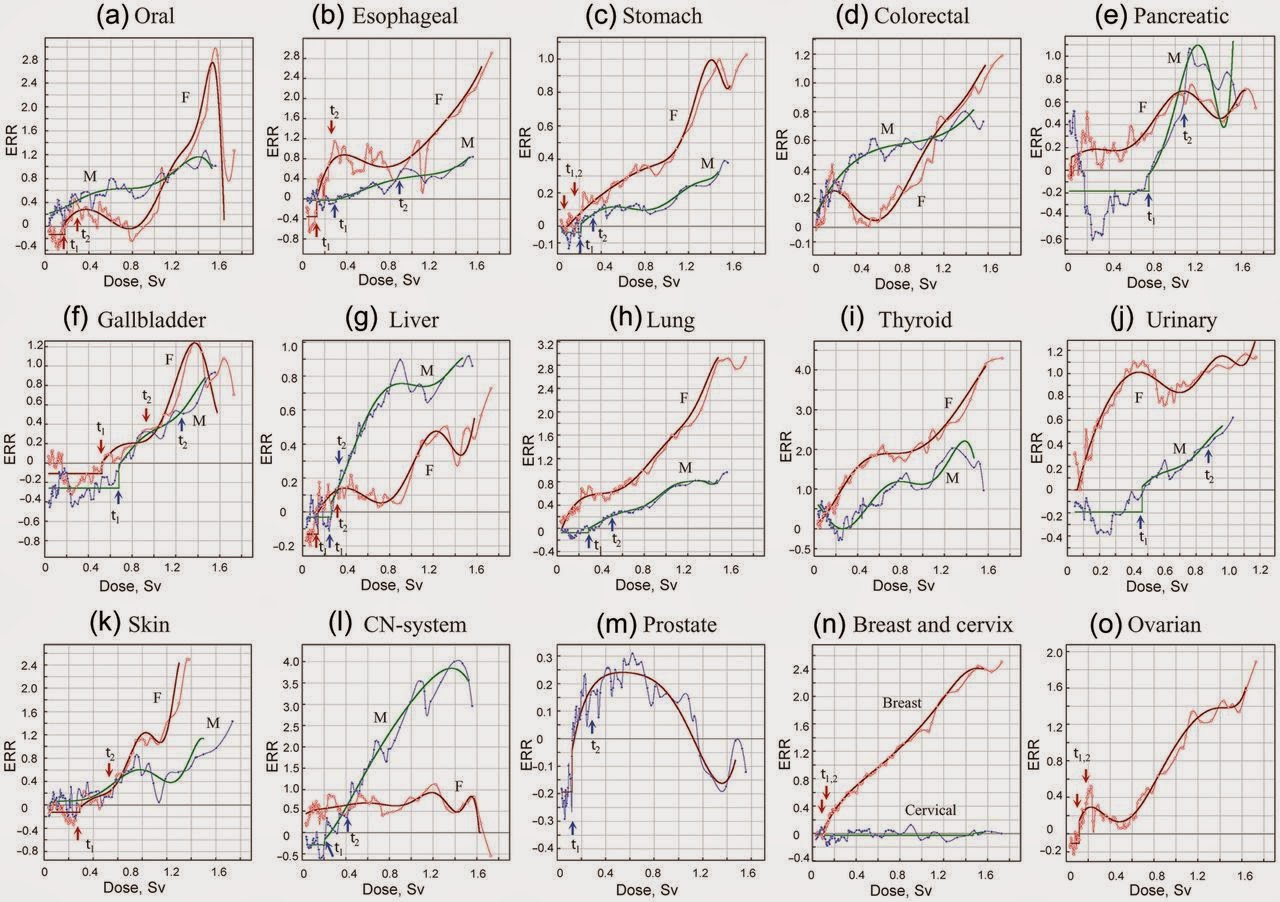
Difference in ERR by gender and organ (Hiroshima). (a) Oral cancer. (b) Esophageal cancer. (c) Stomach cancer. (d)Colorectal cancer. (e) Pancreatic cancer. (f) Gallbladder cancer. (g) Liver cancer. (h) Lung cancer. (i) Thyroid cancer. (j)Cancer of urinary system. (k) Skin cancer (non-melanoma). (l) Brain cancer (cancer of central nervous system). (m)Prostate cancer. (n) Breast and cervical cancer. (o) Ovarian cancer. M = male, F = female.
Liquid cancer. (a) City differences for ERR. (b) Gender difference for ERR in Hiroshima. (c) Gender difference for ERR in Nagasaki (including factory workers) (N − a). (d) Gender difference for ERR in Nagasaki (excluding factory workers) (N − b). (e) The dose–responses after city- and gender-adjustment. For Nagasaki, adjustments were made using non-factory workers. M = male, F = female, H = Hiroshima, N = Nagasaki, T = two cities combined.
2. Dan Yurman – Neutron Bytes – Things that go bump in the night in Idaho
Just in time for Halloween, the fate of a government nuclear energy R and D center appears to tremble on the precipice of change or does it? Only the New York Times knows for sure.
3. Northwest Women in Northwest Nuclear Energy
Energy Northwest (EN) owns several clean energy facilities, including Columbia Generating Station near Richland Washington. EN has recently started a blog: “Northwest Clean Energy.” This blog posts describes the careers of two women nuclear engineers in the Northwest: Wanda Munn was an engineer at the Fast Flux Test Facility, and Kaitlin Carter is part of the Systems Engineering Group at Columbia Generating Station.
In the Northeast, electric rates are rising at an amazing pace (over 40% for one utility, starting today). Vermont Yankee’s closing is part of the reason for this rise, but not the complete reason.
Fukushima evacuees get all the international Press attention, while tsunami refugees are virtually ignored. Reuters has broken the mold and shows that tens of billions of dollars in tsunami recovery money is untouched although less than 10% of residential reconstruction has occurred. If this were happening to Fukushima evacuees, the world’s Press would scream loud and long.
7. Jim Conca – Forbes – America’s Navy The Unsung Heroes Of Nuclear Energy
America’s Nuclear Navy is one of the oldest and largest nuclear organizations in the world, and has the best safety record of any industry. There are over a hundred nuclear reactors that power 86 submarines and aircraft carriers. Thousands upon thousands of people have lived, worked, eaten and slept within a stone’s throw of a nuclear reactor for 60 years with no adverse effects at all.
8. Rick Maltese of The Energy Reality Project – Aiming at a National Energy Policy for Energy Reality
If we were to investigate countries across the globe it would be difficult to find a respectable national energy policy. Energy Reality tries to sort out what is needed as a general guide to all countries. But it is not what you might expect. It involves more than just finding the best energy mix.
9. ANS Nuclear Cafe – Two Pieces of Good News for Nuclear
Jim Hopf breaks down the details regarding the recent DOE announcement on funding advanced reactor design and the recent European ruling on Hinkley Point C.
10. Nextbigfuture – a design for smaller, safer, pressured water reactor that would use thorium
11. Nextbigfuture – Fast and high temperature reactor advantages and developments.

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.