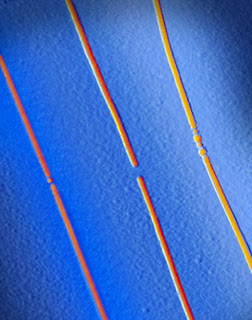
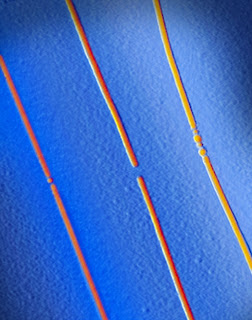
Three parallel memory bits with carbon nanotube electrodes (false color image based on topographic profile from atomic force microscopy). The middle bit is in the “off” state, the other two are “on”. The silicon dioxide substrate is shown in blue. | Image courtesy Eric Pop
Science Express – Low-Power Switching of Phase-Change Materials with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes
Phase-change materials (PCMs) are promising candidates for nonvolatile data storage and reconfigurable electronics, but high programming currents have presented a challenge to realize low power operation. We controlled PCM bits with single-wall and small-diameter multi-wall carbon nanotubes. This configuration achieves programming currents as low as 0.5 μA (SET) and 5 μA (RESET), two orders of magnitude lower than state-of-the-art devices. Pulsed measurements enable memory switching with very low energy consumption. Analysis of over 100 devices finds that the programming voltage and energy are highly scalable, and could be below 1 V and single femtojoules per bit, respectively.
The flash memory used in mobile devices today stores bits as charge, which requires high programming voltages and is relatively slow. Industry has been exploring faster, but higher power phase-change materials (PCM) as an alternative. In PCM memory a bit is stored in the resistance of the material, which is switchable.
Pop’s group lowered the power per bit to 100 times less than existing PCM memory by focusing on one simple, yet key factor: size.
Rather than the metal wires standard in industry, the group used carbon nanotubes, tiny tubes only a few nanometers in diameter – 10,000 times smaller than a human hair.
“The energy consumption is essentially scaled with the volume of the memory bit,” said graduate student Feng Xiong, the first author of the paper. “By using nanoscale contacts, we are able to achieve much smaller power consumption.”
To create a bit, the researchers place a small amount of PCM in a nanoscale gap formed in the middle of a carbon nanotube. They can switch the bit “on” and “off” by passing small currents through the nanotube.
“Carbon nanotubes are the smallest known electronic conductors,” Pop said. “They are better than any metal at delivering a little jolt of electricity to zap the PCM bit.”
Nanotubes also boast an extraordinary stability, as they are not susceptible to the degradation that can plague metal wires. In addition, the PCM that functions as the actual bit is immune to accidental erasure from a passing scanner or magnet.
The low-power PCM bits could be used in existing devices with a significant increase in battery life. Right now, a smart phone uses about a watt of energy and a laptop runs on more than 25 watts. Some of that energy goes to the display, but an increasing percentage is dedicated to memory.
“Anytime you’re running an app, or storing MP3s, or streaming videos, it’s draining the battery,” said Albert Liao, a graduate student and co-author. “The memory and the processor are working hard retrieving data. As people use their phones to place calls less and use them for computing more, improving the data storage and retrieval operations is important.”
Pop believes that, along with improvements in display technology, the nanotube PCM memory could increase an iPhone’s energy efficiency so it could run for a longer time on a smaller battery, or even to the point where it could run simply by harvesting its own thermal, mechanical or solar energy – no battery required.
And device junkies will not be the only beneficiaries.
“We’re not just talking about lightening our pockets or purses,” Pop said. “This is also important for anything that has to operate on a battery, such as satellites, telecommunications equipment in remote locations, or any number of scientific and military applications.”
In addition, ultra-low-power memory could cut the energy consumption – and thus the expense – of data storage or supercomputing centers by a large percentage. The low-power memory could also enable three-dimensional integration, a stacking of chips that has eluded researchers because of fabrication and heat problems.
The team has made and tested a few hundred bits so far, and they want to scale up production to create arrays of memory bits that operate together. They also hope to achieve greater data density through clever programming such that each physical PCM bit can program two data bits, called multibit memory.
The team is continuing to work to reduce power consumption and increase energy efficiency even beyond the groundbreaking savings they’ve already demonstrated.
“Even though we’ve taken one technology and shown that it can be improved by a factor of 100, we have not yet reached what is physically possible. We have not even tested the limits yet. I think we could lower power by at least another factor of 10,” Pop said.
11 pages of supplemental material
If you liked this article, please give it a quick review on ycombinator or StumbleUpon. Thanks

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.